Knee Arthritis
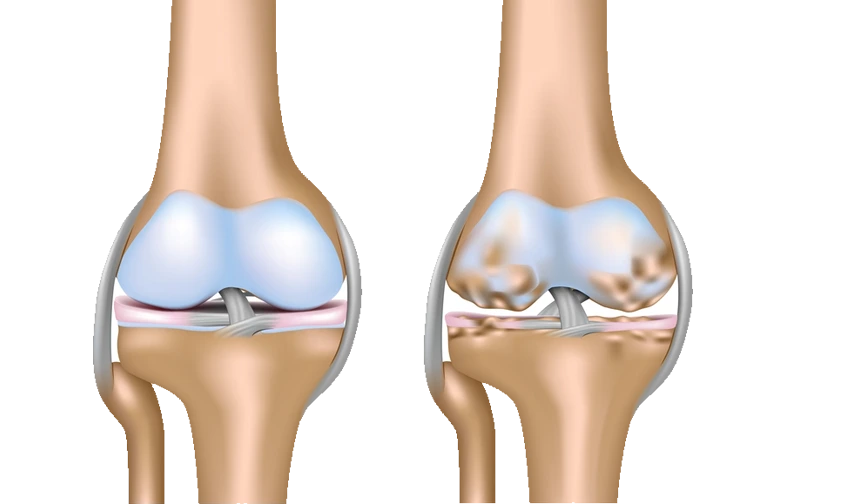
Knee arthritis is the inflammation and breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility. The most common types are osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears away, and rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition. Treatment includes medications, physical therapy, weight management, and, in severe cases, surgery like knee replacement.
Symptoms of Knee Arthritis
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Grinding or Popping Sensations
- Warmth in the Joint
- Increased Discomfort with Activity
- Weakness
Type of Knee Arthritis:
- It Osteoarthritis (OA)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Infectious (Septic) Arthritis
Causes of Knee Arthritis:
Knee arthritis, a common condition, is caused by the breakdown of cartilage in the knee joint. Several factors contribute to its development:
- As people age, the cartilage that cushions the knee joint naturally wears down, leading to arthritis.
- Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joint, accelerating cartilage wear and increasing the risk of arthritis
- Previous injuries to the knee, such as fractures or ligament tears, can lead to arthritis over time.
- Weakness in the muscles around the knee can place more pressure on the joint, leading to arthritis.
- Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, which causes inflammation in the joints, can also affect the knee and lead to arthritis.
Treatments for Knee Arthritis
Knee arthritis, most commonly osteoarthritis, occurs when the cartilage that cushions the knee joint wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and inflammation. Treatments for knee arthritis aim to reduce symptoms and improve function. The approach depends on the severity of the arthritis and may include the following options:
- Weight Management: Reducing body weight can significantly lessen the load on the knees, relieving pain and slowing progression.
- Exercises: Low-impact activities (walking, swimming, cycling) help strengthen muscles around the knee, improving stability and mobility.
- Range-of-motion Exercises: Help maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness.
- Viscosupplementation
- Partial Knee Replacement (UKA)
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR)

